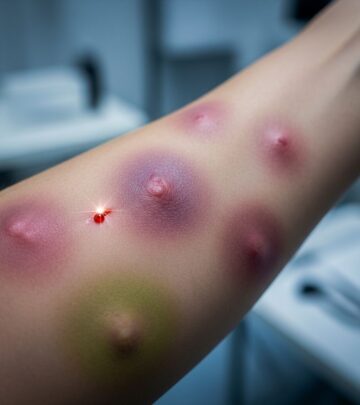
Sonidegib: Treatment for Advanced Basal Cell Carcinoma
Comprehensive guide to Sonidegib (Odomzo), a Hedgehog pathway inhibitor for locally advanced basal cell carcinoma treatment.
Introduction to Sonidegib
Sonidegib, marketed under the brand name Odomzo® and manufactured by Novartis (New Jersey, USA), represents a significant advancement in dermatological oncology. In July 2015, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved this innovative oral medication as the first hedgehog pathway inhibitor specifically designed to address locally advanced basal cell carcinoma (laBCC). The approval followed comprehensive clinical evaluation demonstrating its efficacy in treating one of the most common malignancies in fair-skinned populations.
Basal cell carcinoma accounts for approximately 80% of nonmelanoma skin cancers, with more than 2.8 million new cases diagnosed annually in the United States. While most cases are successfully managed through surgical intervention, advanced cases present significant challenges and often result in substantial morbidity. Sonidegib offers a critical treatment option for patients with locally advanced BCC who are not suitable candidates for conventional surgical or radiation therapy.
What Sonidegib Is and How It Works
Sonidegib is an orally available small molecular inhibitor of the hedgehog pathway, specifically functioning as a smoothened (SMO) antagonist. The medication works through a sophisticated mechanism that targets the root cause of basal cell carcinoma at the cellular level.
The drug’s mechanism of action involves binding to and inhibiting the activity of the SMO transmembrane protein, which is crucial in the hedgehog signaling pathway. This inhibition results in the complete suppression of GLI (glioma-associated oncogene), a transcription factor essential for cellular proliferation in BCC. By blocking this pathway, sonidegib effectively reduces tumor cell growth and promotes regression of existing lesions.
Preclinical studies have demonstrated that sonidegib exhibits high tissue penetration, including crossing the blood-brain barrier, combined with good oral bioavailability. This property ensures that the medication reaches therapeutic concentrations in affected tissues throughout the body, making it particularly effective for treating dermatological malignancies.
Indications and Uses
FDA-Approved Indications
Sonidegib is specifically indicated for the treatment of adult patients presenting with locally advanced basal cell carcinoma in two distinct clinical scenarios:
- Adult patients experiencing recurrence of locally advanced basal cell carcinoma (laBCC) following surgery or radiation therapy
- Adult patients with laBCC who are not amenable to surgical intervention or radiation therapy
These indications are particularly important for patients with extensive tumors involving critical anatomical structures, those with significant comorbidities precluding surgery, or those who have already exhausted conventional treatment options.
Off-Label Dermatologic Uses
Beyond its primary FDA-approved indications, sonidegib demonstrates therapeutic potential in several off-label dermatological conditions. The most significant off-label use involves nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome (previously known as Gorlin syndrome), a hereditary condition characterized by the development of numerous BCCs throughout the patient’s lifetime.
A randomized trial evaluating sonidegib’s efficacy in nevoid BCC syndrome demonstrated remarkable clinical outcomes. Seven patients treated with 400 mg/day sonidegib for 12 weeks exhibited complete clinical clearance in three patients (43%) by week 16, while the remaining four patients experienced at least moderate clinical clearance. Notably, all patients receiving sonidegib 400 mg demonstrated either complete or partial clearance of their target BCCs, with no patient experiencing worsening of lesions.
Topical formulations of sonidegib have also been investigated for Gorlin syndrome treatment. In a study of eight patients with 27 BCCs treated with 0.75% LDE225 topical cream, three BCCs achieved complete response, nine achieved partial response, and only one failed to demonstrate clinical response. However, subsequent larger trials did not reproduce these encouraging results with topical sonidegib, likely due to limited drug penetration across the cutaneous barrier.
Pharmacology and Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetic Profile
Understanding sonidegib’s pharmacokinetic characteristics is essential for optimizing treatment outcomes and managing potential adverse effects. The drug exhibits an estimated 6% oral bioavailability with highly extensive binding to human plasma proteins (>97%), resulting in a remarkably high volume of distribution exceeding 9,000 liters. This extensive distribution throughout body tissues contributes to its therapeutic efficacy, with concentrations in skin reaching six times higher than plasma concentrations.
Sonidegib demonstrates a relatively long half-life of 28 days due to its substantial protein-binding capacity. The median time to peak plasma concentration (Tmax) occurs within 2–4 hours of dosing, with steady-state plasma concentration achieved by week 17 of continuous treatment. This relatively rapid absorption but prolonged elimination profile allows for once-daily dosing and permits cumulative tissue accumulation over the initial treatment period.
A notable distinction exists between sonidegib and vismodegib, its primary competitor in the hedgehog inhibitor class. While sonidegib reaches peak plasma concentration within 2–4 hours and achieves steady state by week 17, vismodegib reaches peak concentration approximately 2 days after a single dose and steady state within 21 days. Sonidegib’s more rapid peak concentration achievement may result in faster clinical response initiation.
Pharmacodynamics
The pharmacodynamic effects of sonidegib directly correlate with its molecular mechanism. Treatment with sonidegib results in decreased GLI levels, reduced GLI-controlled transcription, and ultimately suppressed cellular proliferation. First-in-human dose-escalation phase I studies involving 103 adult patients with advanced solid tumors demonstrated dose- and exposure-dependent inhibition of GLI1 mRNA expression in both tumor and normal skin biopsies.
Dosage and Administration
The standard adult oral dosage of sonidegib is 200 mg administered once daily. This dosing regimen was established based on comprehensive clinical trial data, particularly the pivotal BOLT phase II trial that formed the basis for FDA approval.
In specific clinical situations, such as nevoid BCC syndrome treatment, higher doses of 400 mg daily have been evaluated with reported efficacy. However, the standard 200 mg daily dose remains the approved regimen for locally advanced basal cell carcinoma management and should be the default unless specific clinical circumstances warrant alternative dosing.
The medication is administered as an oral capsule, allowing for convenient once-daily dosing that may enhance patient compliance compared to more frequent dosing schedules. Patients should maintain consistent timing of administration to optimize steady-state plasma concentrations.
Clinical Efficacy
The clinical efficacy of sonidegib was established through rigorous randomized controlled trials. In the pivotal BOLT clinical trial, treatment with sonidegib 200 mg demonstrated a 58% objective response rate. This response rate comprised complete responses in 5% of patients and partial responses in 53% of patients with locally advanced basal cell carcinoma.
Across multiple studies and randomized controlled trials evaluating sonidegib’s efficacy and safety, the medication has demonstrated a good overall response rate of 44% in various patient populations. These findings reinforce the significant association between hedgehog pathway inhibition and tumor response in advanced basal cell carcinoma.
During treatment with sonidegib, characteristic features of BCC on high-resolution skin imaging techniques have been observed to decrease or disappear completely. This objective imaging evidence supports the subjective clinical responses reported by patients and physicians alike.
Adverse Effects
Most Common Adverse Reactions
Clinical trials have identified specific adverse reactions occurring with significant frequency during sonidegib treatment. The most common adverse reactions (≥10%) associated with sonidegib therapy include:
- Muscle spasms
- Alopecia (hair loss)
- Dysgeusia (altered taste sensation)
- Fatigue
- Nausea
Additional Reported Adverse Events
Beyond the most common reactions, additional adverse effects have been documented in clinical trial populations:
- Musculoskeletal pain
- Diarrhea
- Decreased weight
- Decreased appetite
- Myalgia (muscle pain)
Adverse Event Severity and Management
An important clinical observation is that a large proportion of patients receiving sonidegib report grade 1–2 adverse events and/or abnormalities in blood examinations, with fewer severe (grade 3–4) adverse events described. This relatively favorable safety profile, combined with the documented efficacy in treating advanced BCC, supports sonidegib’s therapeutic utility in appropriate patient populations.
Safety results from clinical trials are comparable across different patient populations, with similar patterns of muscle spasms, alopecia, and dysgeusia consistently reported. Understanding these predictable adverse effects allows healthcare providers to implement appropriate monitoring and supportive care strategies.
Warnings and Precautions
Patients receiving sonidegib therapy should undergo comprehensive baseline assessment and regular monitoring throughout treatment duration. Healthcare providers must carefully evaluate potential drug interactions and contraindications before initiating therapy. Particular attention should be directed toward patients with baseline electrolyte abnormalities, significant hepatic or renal impairment, or those receiving concurrent medications known to interact with hedgehog pathway inhibitors.
Pregnancy represents a critical consideration, as sonidegib may pose risks to fetal development. Women of childbearing potential should employ effective contraception during treatment and for a defined period following cessation of therapy. The specific duration of post-treatment contraception recommendations should be verified with current prescribing information.
Regular monitoring of muscle symptoms is particularly important given the frequent occurrence of muscle spasms. Patients should be counseled regarding expected adverse effects and instructed to report severe or persistent symptoms promptly.
Potential Drug Interactions
Sonidegib’s extensive protein binding (>97%) and high volume of distribution necessitate careful consideration of potential drug interactions. While specific interaction data should be reviewed in current prescribing information, clinicians should exercise caution when combining sonidegib with other highly protein-bound medications or agents that significantly induce or inhibit hepatic metabolism.
Patients receiving concomitant medications should have their regimens reviewed prior to sonidegib initiation to minimize the risk of clinically significant interactions.
Comparison with Other Hedgehog Inhibitors
Vismodegib represents the primary competitor in the hedgehog inhibitor class for advanced basal cell carcinoma treatment. While both medications demonstrate efficacy through SMO antagonism, sonidegib exhibits superior effectiveness in patients with locally advanced BCC compared to metastatic BCC, whereas the comparative performance varies depending on specific clinical presentations.
The distinct pharmacokinetic profiles of these agents may influence clinical decision-making. Sonidegib’s more rapid achievement of peak plasma concentration and earlier steady-state attainment may theoretically allow faster clinical response initiation compared to vismodegib.
Clinical Considerations and Patient Selection
Sonidegib represents a transformative treatment option for patients with locally advanced basal cell carcinoma unsuitable for conventional surgical or radiation therapy. Appropriate patient selection involves identifying those with disease characteristics that pose significant surgical morbidity risks, extensive involvement of critical structures, or prior treatment failure.
The favorable response rate of 58% in the BOLT trial, combined with a relatively manageable adverse effect profile dominated by grade 1–2 events, supports sonidegib’s use as a valuable therapeutic option in advanced BCC management. The demonstrated efficacy in nevoid BCC syndrome further expands its clinical utility for patients with hereditary predisposition to multiple BCCs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How does sonidegib differ from standard BCC treatments?
A: Sonidegib is an oral systemic therapy targeting the hedgehog signaling pathway, differing fundamentally from surgical excision or radiation therapy. It is specifically designed for patients with locally advanced BCC who cannot tolerate or are not candidates for conventional treatments, offering a non-invasive pharmacologic alternative.
Q: What is the expected timeline for seeing treatment response?
A: While individual responses vary, sonidegib achieves steady-state plasma concentrations by week 17 of treatment. Clinical response assessment typically occurs following several months of continuous therapy, with characteristic BCC features on imaging progressively decreasing or disappearing.
Q: Are there any lifestyle modifications needed during sonidegib therapy?
A: Patients should maintain consistent medication timing for optimal therapeutic effect. Women of childbearing potential must use effective contraception. Sun protection remains important, and patients should report new skin lesions or changes in existing lesions to their healthcare provider promptly.
Q: Can sonidegib be used preventatively in high-risk patients?
A: Sonidegib is currently approved for treatment of existing locally advanced BCC, not as preventive therapy. However, off-label use in nevoid BCC syndrome has demonstrated significant efficacy in reducing existing lesion burden in patients with this hereditary condition.
Q: What monitoring is required during sonidegib treatment?
A: Regular clinical assessment of treatment response and adverse effects is essential. Blood examination abnormalities have been documented, necessitating periodic laboratory monitoring. Patients should be evaluated for muscle symptoms, hair loss, taste changes, and other common adverse effects at scheduled visits.
Q: Is sonidegib effective for metastatic BCC?
A: Sonidegib demonstrates greater efficacy in locally advanced BCC compared to metastatic BCC. Patients with metastatic disease may still benefit from treatment, but response rates may be lower than in locally advanced presentations.
References
- Sonidegib Therapeutic Cheat Sheet — Next Steps in Dermatology. 2024. https://nextstepsinderm.com/derm-topics/sonidegib-therapeutic-cheat-sheet/
- Sonidegib: Safety and Efficacy in Treatment of Advanced Basal Cell Carcinoma — PMC, National Center for Biotechnology Information. 2020. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7211768/
- Sonidegib – DermNet — DermNet New Zealand. 2024. https://dermnetnz.org/topics/sonidegib
- Odomzo (Sonidegib), a Hedgehog Pathway Inhibitor, FDA Approved for the Treatment of Patients with Locally Advanced Basal-Cell Carcinoma — AHDB Online. 2016. https://www.ahdbonline.com/issues/2016/march-2016-vol-9-seventh-annual-payers-guide/odomzo-sonidegib-a-hedgehog-pathway-inhibitor-fda-approved-for-the-treatment-of-patients-with-locally-advanced-basal-cell-carcinoma-by-loretta-fala-medical-writer
- ODOMZO (Sonidegib) Prescribing Information — U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 2019. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/205266s006lbl.pdf
Read full bio of Sneha Tete